MFRC522 and Raspberry Pi
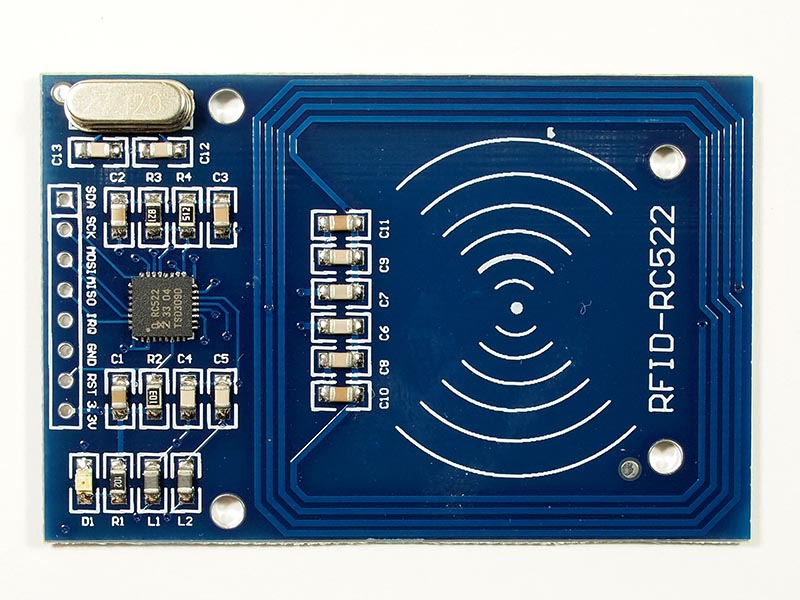
Image Source: http://www.haoyuelectronics.com
Connecting the MFRC522 to RPI
This website has a nice diagram of the RPI pinout: https://pinout.xyz/pinout/pin22_gpio25
| MFRC522 | RPI | Physical Pin |
|---|---|---|
| SDA | 24 | GPIO8 |
| SCK | 23 | GPIO11 |
| MOSI | 19 | GPIO10 |
| MISO | 21 | GPIO9 |
| IRQ | None | None |
| GND | Any | Any Ground |
| RST | 22 | GPIO25 |
| 3.3V | 1 | 3V3 |
Raspberry Pi
Enable SPI with raspi-config. Menu > Interfacing Options > SPI
user@computer$ sudo raspi-config
Add the following to boot.txt with your favorite text editor.
device_tree_param=spi=on
dtoverlay=spi-bcm2708
user@copmuter$ sudo rpi-update
To read and write data to NFC tags you can use this python class: MRFC522 python. The next step is to install SPI-Py which is a dependency of MFRC522 python.
Cloning SPI-Py Github repo
user@computer$ git clone https://github.com/lthiery/SPI-Py
Cloning into 'SPI-Py'...
remote: Counting objects: 81, done.
remote: Total 81 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 81
Unpacking objects: 100% (81/81), done.
Installing SPI-Py
user@computer$ sudo python SPI-Py/setup.py install
Downloading MFRC522 python
user@computer$ git clone https://github.com/mxgxw/MFRC522-python
Cloning into 'MFRC522-python'...
remote: Counting objects: 60, done.
remote: Total 60 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 60
Unpacking objects: 100% (60/60), done.
Reading NFC tag
user@computer$ python MRFC522-python/Read.py
Welcome to the MFRC522 data read example
Press Ctrl-C to stop.
The MFRC522 should work now . . .
This error is raised after executing Read.py
fatal error: Python.h: No such file or directory compilation terminated.
Solution: install python-dev
user@computer$ sudo apt-get install python-dev #python 2
user@computer$ sudo apt-get install python3-dev #python 3
Debugging Java Programs With JDB
JDB is a simple command line Java debugger.
Starting a jdb session
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class example
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList<Integer> x = new LinkedList<Integer>();
x.add(10);
sum();
}
public static void sum()
{
int a = 2;
int b = 3;
System.out.println(a + b);
}
}
user@computer$ javac example.java
user@computer$ jdb example
Initializing jdb ...
>
Breakpoints
Lines
> stop at example:5
Methods
> stop in example.main
Displaying Breakpoints
> clear
Breakpoints set:
breakpoint example:5
breakpoint example.main
Deleting Breakpoints
> clear example:5
Removed: breakpoint example:5
Continue after hitting a breakpoint
> cont
Continue one line
> next
Step into function
> step
Print source code
> list
Run class
> run example
Printing
main[1] dump a
com.sun.tools.example.debug.expr.ParseException: Name unknown: a
a = null
Cannot print or dump variables if class is not compiled with -g option.
javac -g example.java
main[1] dump a
a = 2
main[1] print a
a = 2
Both print and dump can print primitive data types. Print can also evaluate expressions.
main[1] print 2 + 2
2 + 2 = 4
Locals prints all the local variables.
main[1] locals
Method arguments:
Local variables:
a = 2
Printing objects
Using dump on objects will print information about the object.
main[1] dump x
u = {
size: 1
first: instance of java.util.LinkedList$Node(id=432)
last: instance of java.util.LinkedList$Node(id=432)
serialVersionUID: 876323262645176354
java.util.AbstractList.modCount: 1
java.util.AbstractCollection.MAX_ARRAY_SIZE: 2147483639
}
Using print on objects will print the contents of the object.
main[1] print x
u = "[10]"